Geographic information system

A geographic information system is a computer method for collecting, obtaining, monitoring, and displaying Data compared with positions on Earth’s surface. By illustrating unrelated data, GIS can help people and groups understand entirely spatial patterns and associations.
What is Geographic information system?
A structure to organize, communicate, and understand the science of our world.
A geographic information system is a structure for the collection, managing, and examining data. Based on the history of geography, GIS associates many types of data. It describes the spatial location and creates layers of information into visualizations utilizing maps and 3D scenes. With this new facility, GIS presents more in-depth insights into data, such as models, relationships, and positions—helping users make quicker decisions.
Numbers of thousands of organizations in practically every field are working GIS to make maps that communicate, perform inquiry, give information, and solve complex queries around the world. This is transforming the way the world acts.
GIS helps in
- Identify problems
- Monitor change
- Manage and responds to events
- Perform forecasting
- Set priorities
- Understand trends
HOW GIS SOFTWARES CAN HELP US?
Besides GIS technology, people can relate to the locations of various things to discover how they link to each other. E.g., using GIS, a single map could incorporate sites that create pollution, such as factories and sites receptive to infection, such as wetlands and waterways. Such a plan would help people resolve where water supplies are abundant at risk.
Many diverse types of information can be examined and contrasted using GIS. The system can carry data about people, such as population, income, or education level. It can consist of data about the landscape, such as the area of streams, several kinds of vegetation, and Earth. It can combine information about the localities of factories, fields, and institutions, or storm drains, paths, and electrical power lines.
GIS can use each information that combines location. The location can be manifested in many different ways, such as latitude and longitude, address, or ZIP code.
GIS applications comprise both hardware and software modes.
APPLICATIONS OF Geographic information system
These applications may include
Cartographic data
Cartographic data are now in map form and may enter such information as the location of rivers, roads, hills, and valleys. Cartographic data may also introduce survey data and mapping data that can be directly accessed into a GIS.
Photographic interpretation
Photographic interpretation is an essential part of GIS. Photo interpretation requires analyzing aerial photographs and evaluating the features that perform.
Remote sensing
Remote sensing presents another mechanism that can be integrated into a GIS. Remote sensing embraces imagery and other data collected from satellites, aircraft, and drones
Digital data
Digital data can also be inserted into a GIS. Cases of this kind of information are computer data accumulated by satellites that determine land use, the place of farms, towns, and forests.
Table or spreadsheet form
Ultimately, GIS can also connect data in table or spreadsheet form, such as community demographics. Demographics can vary from age, revenue, and ethnicity to new purchases and internet browsing favorites.
GIS works location as the key index variable to link these independent data.
Data capture
Placing information into GIS is called data capture. Data that are previously in digital forms, such as most maximum tables and pictures captured by satellites, can be uploaded into GIS. Maps, however, need first be considered or converted to digital setup.
Types of Geographic information system file
The couple significant models of GIS file forms are raster and vector. Raster formats are grills of cells or pixels. Raster formats help store GIS data that diversify, such as altitude or satellite description. Vector formats are polygons that use circumstances (called nodes) and lines. Vector formats are useful for collecting GIS data with firm boundaries, such as school areas or routes.
Spatial Relationships
geographic information technology can be adopted to represent spatial links and direct networks. Spatial relationships may inspect topography, such as agricultural ranges and rivers. They may also show land-use patterns, such as the area of parks and residential complexes.
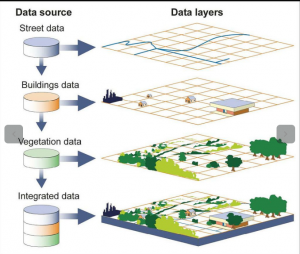
GIS Maps
Once all the aspired data have been inserted into a GIS system, they can be linked to produce a broad type of individual maps, depending on which data sheets are involved. One of the many common uses of GIS technology means connecting natural characteristics with human activity.
For example, GIS maps can reveal what human-made traits are near certain common elements, such as which hotels and companies are in areas inclined to flood.
GIS technology also enables users to “dig deep” in a particular area with several kinds of data. Maps of a specific city or region can relate to average wages, book sales, or voting patterns. Any GIS data-sheet can be joined or deducted to the same map.
GIS maps can be adopted to show information about numbers and quantity. For example, GIS can determine how many professors there are in a neighborhood than the area’s population.
With GIS technology, researchers can also study at turn over time. They can use satellite data to analyze problems such as the rise and retreat of ice cover in polar quarters, and how that coverage has evolved through time. Police confinement might review changes in crime data to help where to assign officers.
One significant use of time-based GIS technology entails creating time-lapse photogrammetry that presents methods occurring over broad areas and long duration. For example, data designating fluid flow in the ocean or air drifts helps scientists quite understand how precipitation and heat energy flow around the globe.
GIS data mining
Geographic information systems or spatial data mining is the use of data mining techniques for spatial data. Data mining, which is the somewhat automated exploration for hidden designs in massive databases, offers vast potential profits for applied GIS-based decision planning. Ideal uses include environmental monitoring. A portion of such information is that the spatial correlation between data dimensions needs specialized algorithms for more efficient data analysis.
Geographic information system & Mapping Software
- ArcGIS Pro 2.4.0
- Business Analyst Desktop
- ENVI
- GeoDa
- QGIS 3.8
- ArcGIS Desktop 10.7.1
Read more GIS