Drones
What is a Drone?
Drones infrequently called “Unmanned Aerial Vehicles” (UAVs) are intended to perform tasks ranging from the mundane to an incredibly-dangerous. These robot-like vehicles could be found to help rescue storm perpetrators in the Swiss Alps, dropping off your grocery items at your front door and nearly everywhere in between. Drones, which were initially designed for the military and aerospace industries, have discovered their way into the mainstream due to the increased levels of safety and effectiveness they bring. These robotic UAVs operate with varying degrees of autonomy without a pilot on board. The level of autonomy of a drone can vary widely from remotely piloted (a human controls its movements) to advanced autonomy, meaning it relies heavily on a sensor system and LIDAR detectors to calculate its movement.
What Kind of technology is being used in drones?
UAV aircraft are fortified with certain technology which is state-of-the-art and include infrared sensors, laser system and GPS, (UAVs for customers, manufacturing, and for the need of the military). A remote ground control (RFC) system is used to control the Drones and are sometimes associated with the ground-based cockpits. There are two parts of an unmanned aerial vehicle device, first is the control system and the second part is the drone itself. collision avoidance systems are presently being used by the latest high-tech drones. To inspect the surroundings Drones, use the latest obstacle detection sensors systems, while the images are turned into 3D mapping by the SLAM technology and programming algorithms that enable the drone to avoid and sense. These systems combine to avoid and sense one or supplementary of the preceding sensors;
- Monocular Vision
- Time of Flight (ToF)
- Lidar
- Infrared
- Ultrasonic
- Vision Sensor
The DJI Mavic 2 Pro and Mavic 2 Zoom have difficulty sensing which is used on entirely six sides. The Mavic 2 practises the both Infrared sensors and Vision which is attached into a vision system which is recognized as an Omni-directional Obstacle Sensing. The DJI Mavic 2 difficulty sensing system is the highest-ranking technology for drones. The objects will sense by Mavic 2, formerly flying around difficulties in forward-facing. When flying backward, it has the ability to do the equivalent, or hover if it is not conceivable or possible to fly around the obstacle. The name of this technology is APAS (Advanced Pilot Assistance System) on the DJI Mavic 2 and Mavic Air drones. The new Drones which are known as Skydio 2 Drone, these Drones were released in December 2019. These Drones also have obstacle circumvention on all edges. The technology of Skydio 2 autonomy computes and visualizes what kind of activities are occurring around the drone. It has the ability to predict perceptively what is going to happen next and it will make the precise conclusions several times a second. 6 x 4k cameras are used by Skydio 2 quadcopter, the purpose is to shape a 3D map of its environs, which will include animals, different kinds of trees, cars, buildings, humans and many more.
What kind of hardware, software, and power supply Drones use?
- Advanced computing technology is used by Drones, from micro controllers to analog controls, single-board computers, and systems-on-chip.
- Autopilot software or flight stack is used in drone applications. Open-source software like Paparazzi, ArduPilot, OpenPilot, and many others which are available easily. Also, there are smartphone apps available for drones.
- Drone use different power sources, including combustion engine, battery system, hydro fuel cell system, solar system, laser system, beam power cable-tethered system, and power supply system. The lithium-polymer battery is the most common source of power in Drones.
Control system of a Drone.
UAVs and drones include hardware and software components for remote control of the aircraft including directly autonomously by an onboard computer or by a pilot. The characteristics of UAV flight are extremely flexible and non-linear, so preserving insolence and steadiness may necessitate non-stop flight system computation and re-adjustment.

Figure1: MOOG Flight Control Computer
Components which are mostly used on surface might be procedure part of a ground control station (GCS) and can include a transmitter and datalink to communicate with the UAV, a controller that is used for manual control of aircraft, and GCS software. Components on boarding the aircraft also contain autopilot, a GCS contact datalink, and peripherals including external scanners and GNSS receivers. When the operating mode is manual, the datalink and modem will relay commands to the UAV from the controller and other GCS controls to enable the aircraft systems needed. The pilot is authorized to automatically regulate the aileron, elevator, throttle, and rudder, for fixed-wing UAVs. If the control is manual it can work on the rudder, collective pitch, cyclic, and throttle for helicopter UAVs.
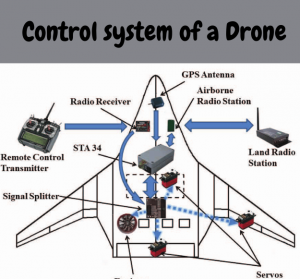
Figure2: Control system of a Drone.
The use of advance and speedy technology in Drones.
The propulsion system (engines, electronic speed controls, and propellers) is the drone technology that takes the UAV into the air and flies in either position or hovering. The motors and propellers operate on a quadcopter in pairs of 2 motors/propellers rotating in a clockwise direction (CW Propellers) and 2 Counter Clockwise (CCW Propellers) rotating motors.
Highly advanced UAV drone include the below mentioned components;
- Motor Stator system
- Bearings
- The system of Motor Bell
- Propellers
- Wiring
- Winding
- Arm
- The system of Electronic Speed Controllers
- ESC Updater system
- Cooling System
The ESC signal provides the information about the speed, braking as well as provide monitoring and fault-tolerant on the drone engines to the drone motors.
Drone Technology Adopting FPV Live Video Transmission.
FPV stands for “First Person View.” On the unmanned aerial vehicle, a video camera is mounted, and this camera transmits the live video to the ground operator. The surface pilot flies the aircraft as if they were inside the plane, rather than looking at the plane from the real ground location of the pilot. First Person View leads to supplementary precise and accurate flying, mostly around difficulties’ makes it very convenient for the unmanned aerial vehicles to hover inside or indoor, or over woods and around houses. Using radio signals to receive and transmit live video, this FPV technology the drone has a built-in wireless transmitter and an antenna which is a multi-band FPV. The recipient of the video signals which are live may be moreover the device which is remote-control, it could be a monitor, it could be also an iPad or a mobile phone device, but this is based on the drone. This feed of live video is associated with signal strength between the drone’s ground control system. The DJI Mavic 2 landscapes 5 miles which is almost 8 km FPV live streaming set with 1080p quality transmission of video. Previous UAV drones for example Phantom 4 Pro and DJI Mavic, can broadcast a video which is live and up to 7 km away. The Inspire 2 and Phantom 4 Pro are using the new system of transmission from DJI Lightbridge 2. DJI Mavic is using smart algorithms and integrated controllers to establish a novel standard for high-definition wireless image distribution by reducing inexpression and cumulative the extreme maximum assortment and inspiration.
