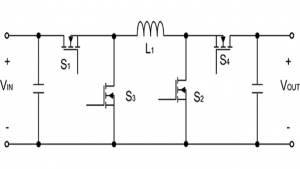
Buck Converter
What is Buck Converter ?
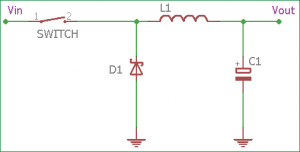
The Buck converter is a type of switched voltage regulator whose voltage level is lower than the input voltage. It uses an inductor to store energy, a capacitor to reduce ripple in the output voltage and a load. The voltage can only be changed by using the duty cycle of the switch, which is driven by a pulse generator. An isolated buck converter is a more efficient form, which provides protection lacking in the non-isolated topology while retaining the functions that make it so unique. The buck converter transfer function is as follows:
VoVin= D.
Where D represents the duty cycle, and Vo and Vin stand for output and input voltage respectively.
The duty cycle ranges from 0 to 1. For instance, if we put 0.5 duty cycles, which means the switch ticks 50 percent for the whole time interval. Let’s suppose the input voltage is 10, we would get an output voltage of 5 volts. Sweet, isn’t it.
History and Advantages of Buck Converter.
Voltage regulation became an important topic in the mid 1900’s, when the landscape of power conversion was in its infancy. The research and development across different spectrum of the subject gave rise to methodical techniques involved in helping achieve better performance. The typical voltage regulator became available with advancement in semiconductor technology. The dependency on ohm’s law was good for the less complex power systems, however, the limitation of a single voltage output proved unfruitful in certain departments which required a broader access to different voltage values. This instilled a necessity for a unique circuitry, which could perform the intended task with the same amount of efficiency as the typical voltage regulator. The advent of Buck converters was relatively new, picking up steam in the late 1940’s, however, it was the 60’s and 70’s that truly caused it to blossom in the form of commercial usage. It was innovative in a sense that not only did it provide the client with better functions, but also increased the degree of freedom. Nonetheless, every device has its own shortcomings. The buck converter, albeit its cheap cost and compactness required multiple components. Ripples and harmonic distortion marred the device which could be reduced by a capacitor. These capacitors and inductors used in itself fulfilled the requirement, but contributed to the size increase and efficiency reduction. It was much later that research in digital electronics subsided the use of such elements altogether. However, its usage could be limited to special equipment.
Linear regulators, which depended on temperature had an innate disability to blow up at a relatively small current increase. The protection scheme was void and this initiated a useless breakthrough making the safety system more expensive. Nonetheless, the cost benefit propelled it across generations, as nowadays, one can find it anywhere in a typical electronic shop. The data sheet provides a plethora of important information. Funny that the data sheet costs more than the device. The buck converter on the other hand is not so prevalent, yet the equipment and guideline available with a tidbit of C++ programming can easily create a shaggy, but formidable circuit. The market for dc-dc converter is increasing and is typically a core subject of the power electronic niche. It’s the future and suppliers have started to shape the supply chain accordingly. Unfortunately, developing countries still do not possess the infrastructure to propel this product. They still need to project it in universities, where grid lines and stations hold more importance than a small circuit. They overlook the endless possibilities and create a gap that the later generation has to fill, but hope it’s not late when the time comes.
Uses and development:
The technologically sophisticated market is ripe for such circuits. The usages ranges from military technology to a solar power system. It is an essential product in mobile phone chargers, which requires a delicate voltage to recharge. The grid supply is static, thus, it needs a mode to reduce the level to one required by the mobile phone. The Buck converter provides such a function.
The research and development over the years has perfected it in terms of efficiency in relation to the system it is used in. Even so that inductor free Buck converters have been developed.
Types of Buck converter:
Dc-Dc Buck converter: This is a specific model used in converting a direct current input voltage to an output voltage. For instance, a power audio amplifier is a great example, in which the increase or decrease in voltage affects the speaker loudness.
Ac-Dc Buck converter: A typical example is a rectifier, which is used in battery chargers. The socket supplies 220V which must be first converted to a Dc waveform and then lower to the required voltage.
Dc-Ac Buck converter: This is a classification called inverter, which is a part of the converter family. The usage consists of Uninterrupted power supply but not limited not. It’s not per se a Buck converter, but comes under the umbrella as Buck converter is a vast field itself.
Modes of Operation:
The Buck converter consists of three modes of operation. First and the most important, which is also known as continuous conduction mode, where the effect of increasing or decreasing the output load does not change the voltage level across it. Then comes the discontinuous conduction mode, where the change load produces different voltage values. There is a lesser known model called the boundary conduction mode, which performs its function just at the boundary in between the other two conduction modes.
Conclusion:
The buck converter which has created a whole new revolution in the electrical field and cost less than a dollar at 95 percent efficiency is worthwhile if the requirements are known to the user. It is a great device with a simple switching program, which can be stored in a micro controller and subsequently is the brain of the whole device. A layman with the passion and intent can easily produce such a potent circuit, which can then be used in a wide range of applications. A few articles will be geared toward making an individual knowledgeable enough to wield the power to create and even improving this exemplary converter.